The 7 Wastes: Unseen Thieves in Your Business
In the world of lean manufacturing, ‘The 7 Wastes’ are infamous for their stealthy operations, silently chipping away at profits and productivity. These wastes fly under the radar, often going unnoticed by even the most astute professionals. Yet, if left unchecked, they can cripple an organisation’s ability to remain competitive and responsive to customer demands.
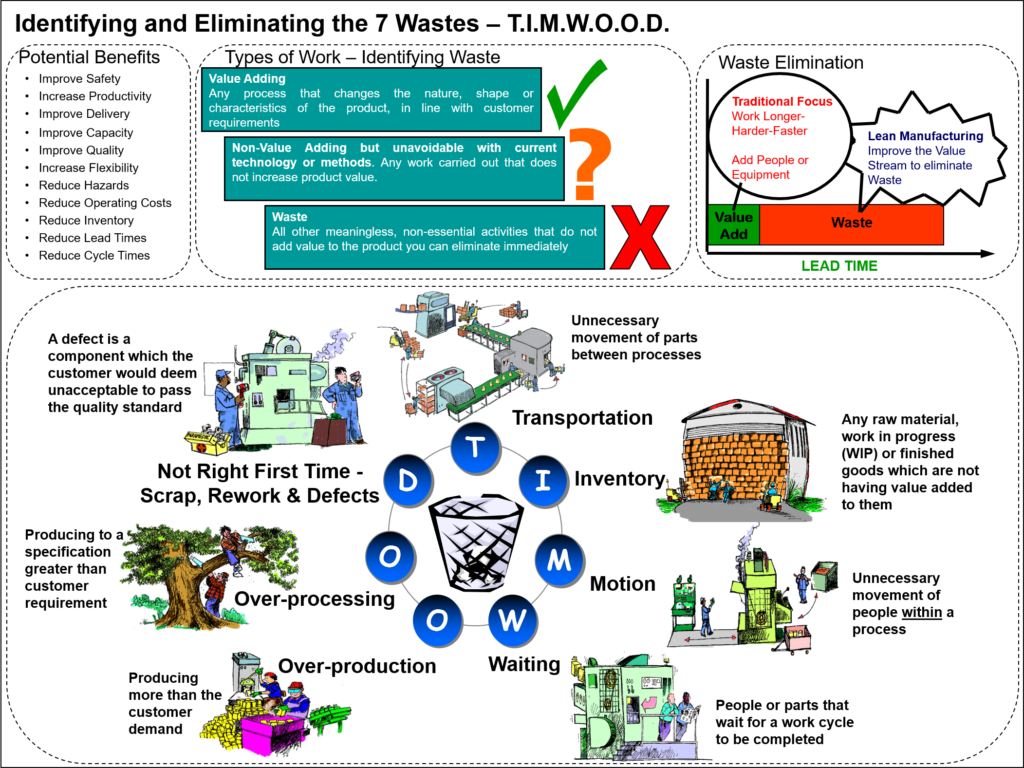
The Infamous Seven: TIMWOOD
Meet the hidden culprits named TIMWOOD, an acronym that represents the seven wastes in manufacturing:
Transport (Unnecessary Movement of Materials)
The unnecessary movement of materials from one place to another is often the result of poor shop layout or a disjointed process flow. This waste can lead to an increase in handling which may cause damage or loss of materials, delays, and added labour costs. Eliminating this waste requires a streamlined approach to layout design and process flow optimisation.
Inventory (Excess Products and Materials)
Excess inventory is a common issue where production outpaces demand, leading to tied-up capital, storage costs, potential obsolescence, and increased risk of damage or loss. Inventory levels should be scrutinised, and techniques such as Just-in-Time (JIT) production and demand-driven planning should be considered for improvement.
Motion (Unnecessary Movement by People)
Similar to Transport, Motion refers to any movement by employees that does not add value to the product. This can range from reaching for tools to walking between workstations. Reducing unnecessary motion is integral to improving ergonomic conditions and efficiency. This reduction can be achieved by redesigning workspaces to minimise reach and travel distance and by standardising work procedures.
Waiting (Idle Time)
When employees or machines are idly waiting for the next step in production, this represents a significant waste of time and resources. This can be due to poor workflow, machine breakdowns, or bottlenecks. Tackling this waste involves a thorough analysis of processes to synchronise work steps and to ensure a continuous flow.
Overproduction (Producing More Than Needed)
Manufacturing items before they are actually required or in quantities exceeding customer demand results in overproduction – the root of many other wastes. This can lead to excessive inventory and increased holding costs. To nip overproduction in the bud, implement pull systems based on real customer demand.
Over-Processing (More Work Than Required)
Over-processing is seen when more work is done on a product than what is valued by the customer. This waste occurs due to unclear customer specifications or internal miscommunication. Reducing over-processing demands a clear understanding of what the customer values and aligning the production process to those standards.
Defects (Production that Requires Rework)
Defects and the need for rework can be the most apparent and costly form of waste. They lead to wasted materials, labour, and time, not to mention the potential to harm a business’s reputation. A culture focused on quality—like adopting Six Sigma or Total Quality Management (TQM)—can significantly curtail the occurrence of defects.
Identification and Elimination Strategy
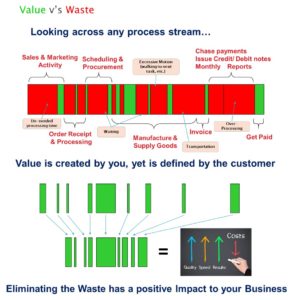
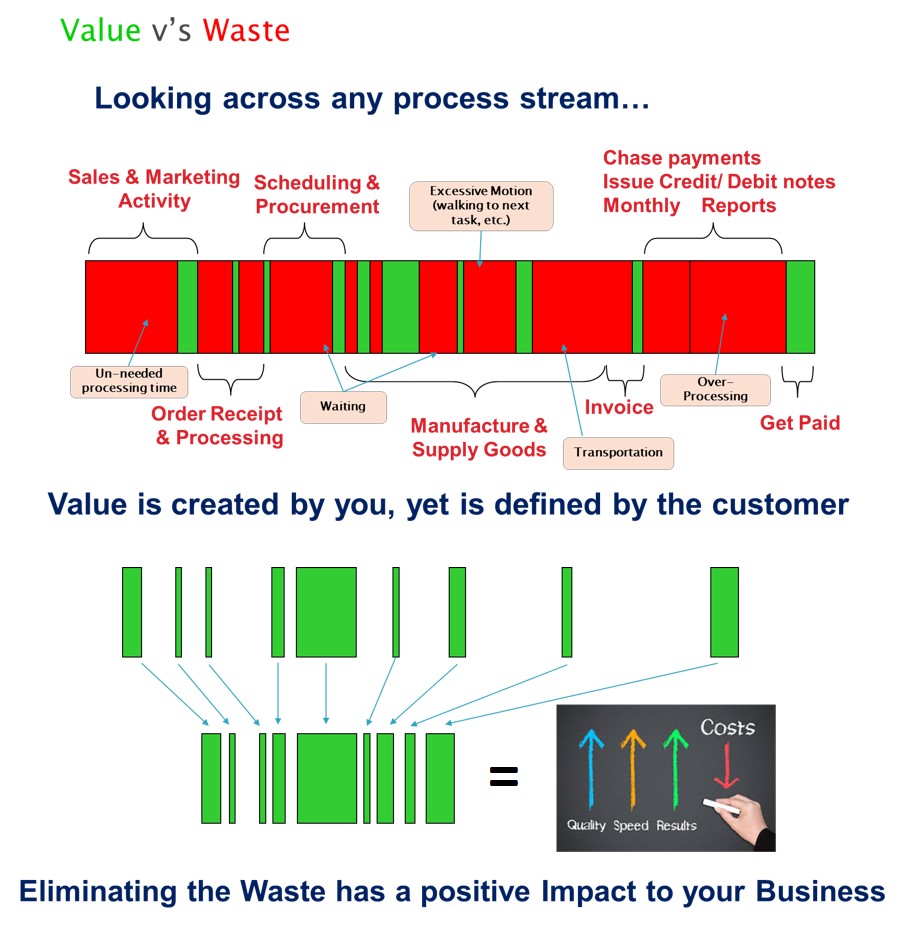
Recognising ‘The 7 Wastes’ is the first step to effective lean management. It’s essential to develop a keen eye for these wastes and instil this perspective across all levels of the organisation. This is not a “once in a blue moon” activity but a regular practice that should be embedded into the daily routine. Regular audits, employee training, and a culture that promotes continuous improvement are key factors for success.
To embed this practice, create a system of visible metrics and feedback loops. This promotes responsibility and awareness amongst teams. Engage employees in problem-solving and encourage them to take ownership of their workspaces, suggest changes, and implement improvements.
Continuous Improvement: The Lean Way
To enter into a sustainable cycle of continuous improvement, adopt the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) methodology. Regularly plan improvements, do them in controlled conditions, check the outcomes, and act to standardise and stabilise the improvements.
Key Takeaways
Employing strategies to eliminate the wastes identified by TIMWOOD ensures a company’s ability to thrive in today’s competitive marketplace. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, providing employee education, and implementing systems that promote efficiency, companies can not only identify waste but turn it into opportunity – for growth, for innovation, and for delivering value to customers that rivals cannot match.
If you need help applying these principles and taking practical steps towards eliminating waste, our team at TCMUK Limited is equipped to guide you through the process. The impact of addressing ‘The 7 Wastes’ can be profound. Call us at 0330 311 2820 or email info@tcmuklimited.co.uk to unlock the full potential of lean in your operation.
Sharing insightful methodologies for operational excellence is at the core of what we do. If you found this article useful, please share it with your networks. We encourage feedback and welcome any questions. Feel free to connect on LinkedIn or reach out to continue the conversation on optimising your business processes.
0330 311 2820
More Blog Posts







To leave me a message or book a return call at a time that suits you