Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) make up a significant portion of the manufacturing sector in the UK, and they play a crucial role in driving economic growth and job creation. However, with increasing competition and rapidly evolving technologies, it’s becoming more important than ever for SME manufacturers to innovate in order to stay competitive and achieve long-term growth.
Innovation can take many forms, from developing new products and processes to improving existing ones. By embracing innovation, SME manufacturers can unlock new markets, enhance their production capabilities, and create more value for their customers. Here are some key ways in which innovation can help drive growth in SME manufacturers with two approaches discussed in each section:
Product Innovation
Product innovation is a key way for SME manufacturers to differentiate themselves from competitors and capture new markets. This involves developing new products or improving existing ones in response to changing customer needs, market trends, or technological advancements. Product innovation can take many forms, such as improving product performance, adding new features, or developing new product lines.
One approach to product innovation is to engage with customers to understand their needs and pain points. This can involve conducting market research, surveys, or focus groups to identify gaps in the market and areas where innovation is needed. SMEs can also leverage social media and online platforms to gather customer feedback and insights.
Another approach is to invest in research and development (R&D) to develop new technologies or materials that can be used to create innovative products. This can involve collaborating with universities, research institutions, or other companies to access new knowledge and expertise. SMEs can also explore government funding and grants to support their R&D efforts.
Process Innovation
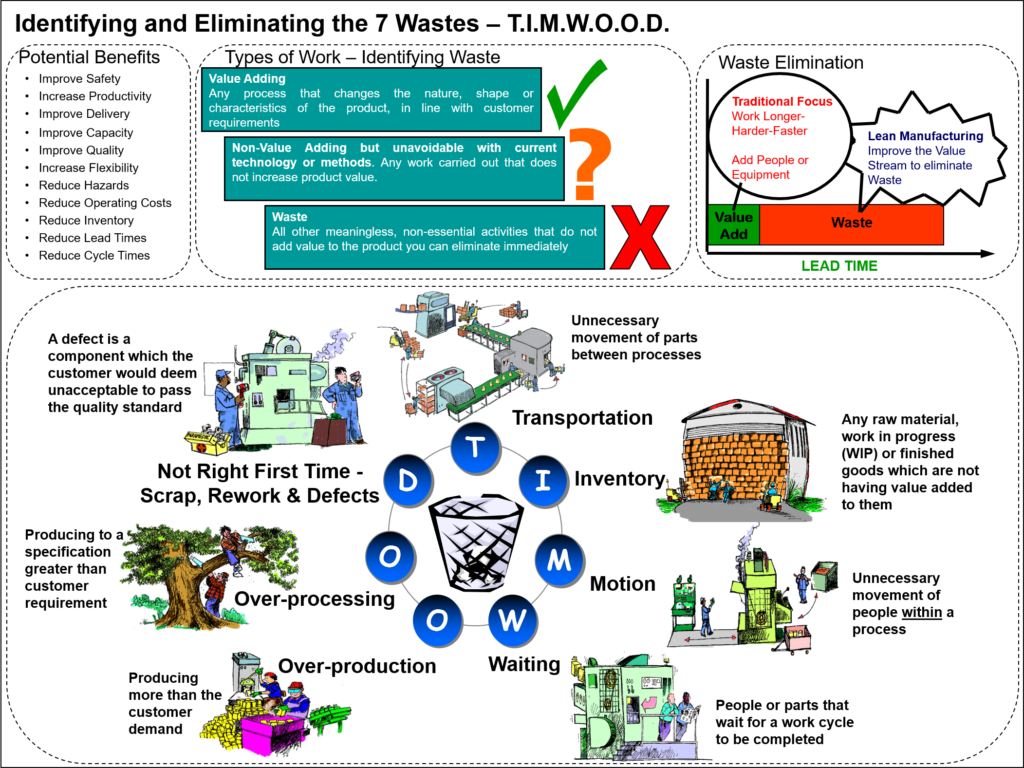
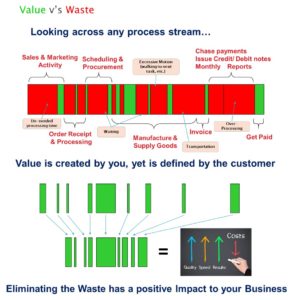
Process innovation involves improving manufacturing processes to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality. This can be achieved through the adoption of new technologies, automation of processes, or the streamlining of workflows. By implementing process innovation, SMEs can become more agile and responsive to market demands and achieve higher levels of productivity and profitability. (For further reading on process innovation or improvement – click here)
One approach to process innovation is to leverage digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, or the internet of things (IoT) to automate processes and enhance decision-making. This can involve implementing smart sensors and devices that can collect and analyse data in real-time, enabling SMEs to optimise their processes and identify opportunities for improvement. (For further information about Digital Technologies check-out 7 Digital Technologies that will Transform Your Factory)
Another approach is to adopt lean manufacturing principles, which refers to eliminating waste from the production process. One way to do this is through continuous improvement programs like Six Sigma or Kaizen. These programs enable you to systematically identify areas for improvement and implement changes.
Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation involves developing new revenue streams or business models that can drive growth and increase profitability. This can involve exploring new markets, developing new distribution channels, or offering new value-added services.
One approach to business model innovation is to develop a subscription-based service that offers customers ongoing value and generates recurring revenue for SMEs. This can involve offering a service that complements existing products or developing a new product that is sold on a subscription basis.
Another approach is to explore online marketplaces or e-commerce platforms to reach new customers and expand the SME’s reach. SMEs can also leverage social media and other digital marketing channels to build brand awareness and generate leads.
Collaborative Innovation
Collaborative innovation involves partnering with other companies, universities, or research institutions to access new ideas, technologies, and resources. This can help SMEs develop breakthrough products or processes that would be difficult to achieve on their own.
One approach to collaborative innovation is to engage in open innovation, which involves collaborating with external partners and crowdsourcing ideas. This can involve setting up innovation challenges or hackathons to encourage the development of new ideas or products.
Another approach is to develop strategic partnerships with other companies or research institutions to access new knowledge or resources. This can involve forming joint ventures or licensing agreements to share expertise and resources.
Open Innovation
Open innovation involves collaborating with external partners and crowdsourcing ideas to accelerate innovation efforts. This can involve engaging with customers, suppliers, or other stakeholders to tap into a broader pool of knowledge and expertise.
One approach to open innovation is to engage in co-creation, which involves collaborating with customers to develop new products or services. This can involve setting up user communities or customer advisory boards to gather feedback and insights.
Another approach is to leverage open innovation platforms or networks to access a wider pool of ideas and resources. SMEs can also participate in industry events or conferences to network with other professionals and share best practices for innovation.
In order to successfully implement open innovation, SMEs should create a culture that values and encourages innovation. This can involve setting up an innovation team or department, providing training and resources for employees to develop their innovation skills, and incentivising and rewarding innovation efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, innovation is a critical driver of growth for SME manufacturing businesses in the UK. By adopting an innovation mindset, SMEs can stay ahead of the competition, create more value for their customers, and achieve long-term success. Whether through product innovation, process innovation, business model innovation, collaborative innovation, or open innovation, SMEs have many options to explore and unlock their full potential.